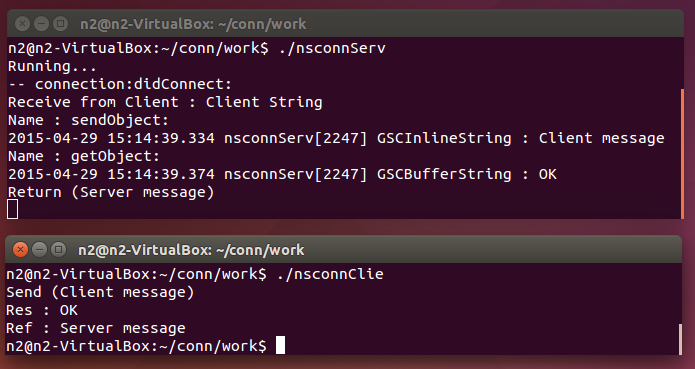
前回のRemoteProcedureCallに似たしくみで、Objective-Cにも同様のリモート呼び出しの仕組みがありましたので、テストしてみました。
Objective-Cのダイナミックな特性により、リモートメソッドもローカルとかわらない方法で呼び出せるところが興味深いです。
環境 : GNUStep / Ubuntu 14.04
protocol.h
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
#include <Foundation/NSConnection.h> @protocol ServerProtocol - (id) sendObject: (id)str; - (void) getObject: (id *)str; - (id) sendString: (const char *)str; @end |
nsconnServ.m
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 |
#include <Foundation/Foundation.h> #include "protocol.h" @interface Server : NSObject <ServerProtocol> { } @end @implementation Server - sendString: (const char *)msg { printf("Receive from Client : %s\n", msg); fflush(stdout); return self; } - sendObject: (id)str { printf ("Name : %s\n", GSNameFromSelector(_cmd)); NSLog(@"%s : %@", GSClassNameFromObject(str), str); fflush(stdout); return @"OK"; } - (void) getObject: (id *)str { static NSString *ret = @"Server message"; printf ("Name : %s\n", GSNameFromSelector(_cmd)); NSLog(@"%s : %@", GSClassNameFromObject(*str), *str); *str = ret; printf("Return (%s)\n", [*str cString]); fflush(stdout); } - connectionBecameInvalid: notification { return self; } - (NSConnection*) connection: ancestor didConnect: newConn { printf("-- %s\n", GSNameFromSelector(_cmd)); [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver: self selector: @selector(connectionBecameInvalid:) name: NSConnectionDidDieNotification object: newConn]; [newConn setDelegate: self]; return newConn; } @end int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { id srv = [[Server alloc] init]; NSAutoreleasePool *arp = [NSAutoreleasePool new]; id pchk = [NSProtocolChecker protocolCheckerWithTarget: srv protocol: @protocol(ServerProtocol)]; NSPortNameServer *ns = [NSSocketPortNameServer sharedInstance]; NSPort *port = [NSSocketPort port]; NSConnection *conn = [NSConnection connectionWithReceivePort: port sendPort: port]; [conn setRootObject: pchk]; [conn registerName: @"nsconnServer" withNameServer: ns]; [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver: srv selector: @selector(connectionBecameInvalid:) name: NSConnectionDidDieNotification object: conn]; [conn setDelegate: srv]; printf("Running...\n"); [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] run]; [arp release]; return 0; } |
nsconnClie.m
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
#include <Foundation/Foundation.h> #include "protocol.h" int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { NSAutoreleasePool *arp = [NSAutoreleasePool new]; NSPortNameServer *ns = [NSSocketPortNameServer sharedInstance]; id proxy = [NSConnection rootProxyForConnectionWithRegisteredName: @"nsconnServer" host: @"" usingNameServer: ns]; Protocol *ps = @protocol(ServerProtocol); [proxy setProtocolForProxy: ps]; [proxy sendString: "Client String"]; NSString *msg = @"Client message"; printf("Send (%s)\n", [msg cString]); id obj = [proxy sendObject: msg]; printf("Res : %s\n", [[obj description] cString]); [proxy getObject: &obj]; printf("Ref : %s\n", [[obj description] cString]); [arp release]; return 0; } |
コマンド
apt-get install gnustep
apt-get install gnustep-devel
gccgnustep-config --objc-flagsnsconnServ.m -lobjc -lgnustep-base -o nsconnServ
gccgnustep-config --objc-flagsnsconnClie.m -lobjc -lgnustep-base -o nsconnClie
パケットキャプチャ
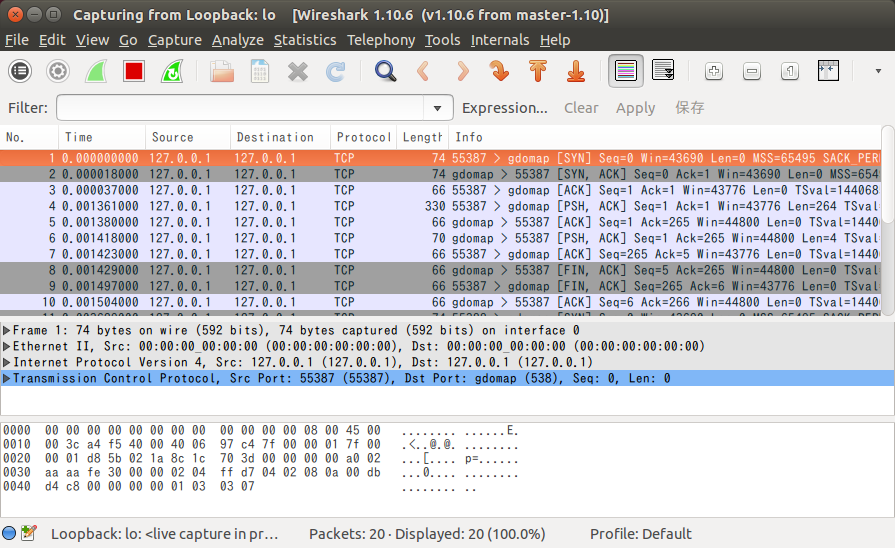
gdomapサービスが、サーバとクライアントの通信を仲介します。これはUbuntuでgnustepをインストールすると自動的にたちあがります。
nsconnServが立ち上がると、gdomapサービスにアクセスし、nsconnClieからのリクエストまちになります。ポート番号は指定していないので、nsconnClieが起動時gdomapサービスにアクセスしたときに、通知されると思われます。
参考:https://github.com/timburks/gnustep-base